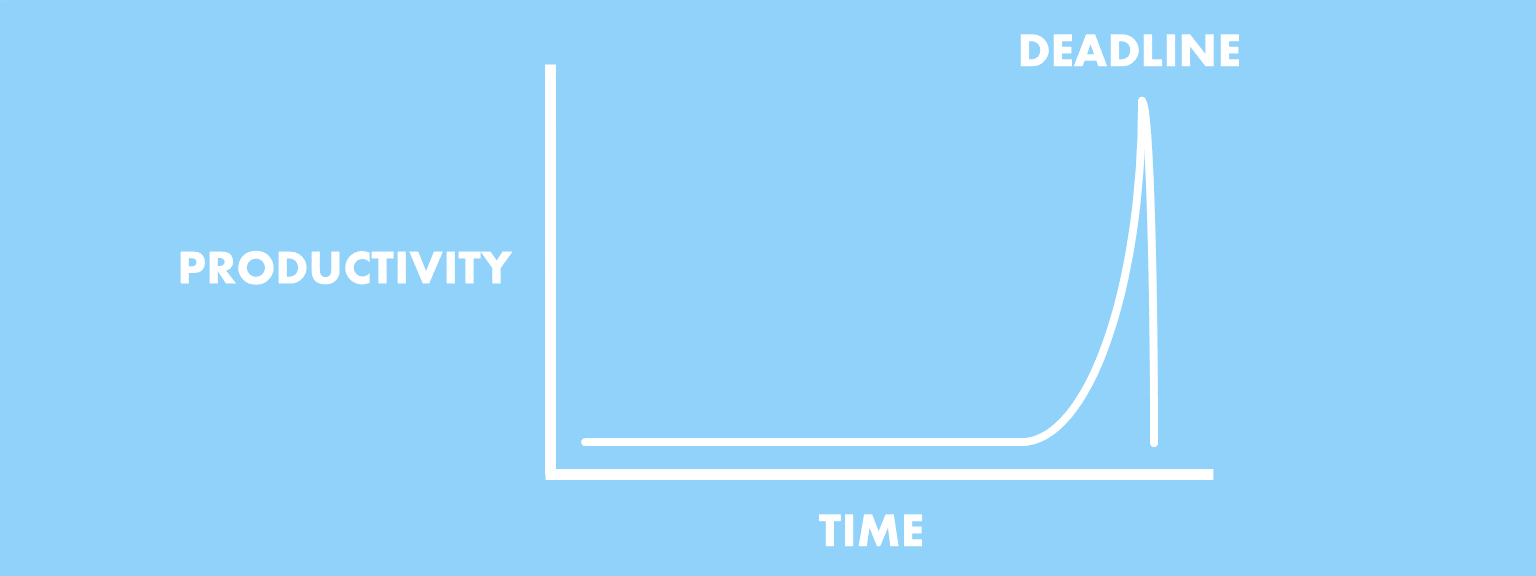
The student syndrome is a phenomenon where people delay doing things until right before the deadline. For example, a student who postpones working on an assignment until the night before it’s due is displaying the student syndrome.
This behavior is called the “student syndrome” because of how common it is among students. However, people other than students often also display it, for example when it comes to workplace projects.
Because the student syndrome is common, and because it can lead to various issues, such as worse performance and increased stress, it’s important to understand it. As such, in the following article you will learn more about this phenomenon and its causes, and see what you can do to deal with it in practice.
Procrastination and the student syndrome
The student syndrome is a form of procrastination, because it involves unnecessary delay, which is often unintentional, and which can be expected to cause negative outcomes for those who display it.
Accordingly, and because this behavior is highly characteristic of procrastinators, questionnaires that are used to diagnose procrastination often contain statements that reflect the student syndrome. This includes, for example, “When I have a deadline, I wait till the last minute” and “I do not do assignments until just before they are to be handed in”.
Examples of the student syndrome
A classic example of the student syndrome is a student who has a week to do a homework assignment, but delays getting started until hours before they have to hand it in.
Similarly, another example of the student syndrome is a student who postpones getting started on an important class project for an entire semester, and then rushes to complete it all the day before it’s due.
In addition, people other than students can also display the student syndrome. For example, a college professor might postpone grading papers until a few hours before the grades are due. Similarly, a manager who has to write an important workplace report might postpone working on it until right before the deadline for completing it.
Note: The student syndrome is often discussed in the context of project management, and the name for this phenomenon was coined in a 1997 book on the topic (“Critical Chain”, by Eliyahu Goldratt).
Dangers of the student syndrome
The student syndrome can lead to various issues, such as:
- Missed deadlines and opportunities. Waiting until right before the deadline to get started can cause people to miss the deadline, especially if the work takes longer to complete than they expected. This is because people who display the student syndrome often wait until they have the minimum amount of time left to complete tasks, which means that they have no safety margin if they misjudge how long it will take to complete the task, or if they experience any unexpected delays occur.
- Worse performance. Even in cases when people manage to complete their work on time despite the student syndrome, they often produce lower-quality work than they would otherwise, due to their rush to get things done under time pressure, or due to issues such as not having enough time to ask clarifying questions.
- Increased emotional, mental, and physical issues. For example, delaying until right before the deadline despite intending to get started earlier can cause people to feel frustrated and stressed. Similarly, staying up late in order to finish tasks the night before they’re due can lead to issues such as lack of sleep and exhaustion.
- Increased interpersonal issues. For example, if someone waits until right before the deadline to complete their part of a group project, their team members might get angry at them. Similarly, if someone always delays until the last possible moment before taking care of household chores, their partner might be frustrated with them.
In addition, note that procrastination is, in general, associated with various related issues, such as worse academic outcomes, worse employment and financial status, worse emotional wellbeing, worse mental and physical health, and a delay in getting treatment for one’s problems.
Prevalence of the student syndrome
There are no statistics regarding the prevalence of the student syndrome in particular. However, given that the student syndrome represents a common form of procrastination (involving an unnecessary delay in getting started on tasks), its prevalence can be estimated based on that of procrastination.
Studies show that procrastination is a very common phenomenon among students, as approximately 80%–95% of college students engage in procrastination to some degree, approximately 75% consider themselves to be procrastinators, and approximately 50% say that they procrastinate in a consistent and problematic manner. Furthermore, additional studies have found procrastination in various other student populations, including those in elementary school, middle school, and graduate school.
In addition, procrastination is also common in other populations, and it chronically affects around 20% of adults.
Psychology and causes of the student syndrome
The student syndrome has many potential causes, which have to do with why people procrastinate in general. Most of these involve the following:
- Motivational problems. These can include issues such as abstract goals, discounting of future outcomes, difficulty in associating tasks with outcomes, and prioritization of enjoyable activities.
- Psychological obstacles. These can include issues such as anxiety, fear of failure, fear of negative feedback, uncertainty, and task aversion, as well as associated issues such as self-handicapping and resentment.
These issues can lead people to delay unnecessarily, even in cases where they intend and want to get started on their work. However, in the case of the student syndrome, as the deadline for a task approaches, people’s mental state changes in a way that prompts them to finally get to work.
For example, as the deadline for a school project approaches, the value of the future outcomes that are associated with it becomes clearer, whether it’s the reward of getting a good grade or the punishment of getting a bad one, which can push students to get started. Similarly, while a person’s aversiveness toward a task may cause them to procrastinate on it initially, the increased time pressure that they experience as the deadline approaches (e.g., due to the increased valuation of the associated outcomes) can become substantial enough that it pushes them to start working on the task, even if their aversion to it hasn’t changed.
Note that a person can display the student syndrome due to a combination of these causes. For example, this can happen if someone suffers both from task aversion and abstract goals.
Furthermore, some of these issues may be caused or exacerbated by other underlying issues. For example, a person’s anxiety may be exacerbated by sleep deprivation. Similarly, a person’s depression may lead them to discount future outcomes and consequently to feel entirely unmotivated.
Finally, some people display the student syndrome, at least in part, due to a preference for working under pressure. For example, this can involve someone deliberately putting off a task until right before the deadline because they feel that they concentrate better when they work under intense time pressure. This type of behavior has been conceptualized in various ways, some of which are controversial, including sensation seeking, arousal procrastination, arousal delay, and active procrastination.
Related concepts
A key phenomenon that underlies the student syndrome is temporal discounting, whereby people tend to discount outcomes that involve a delay. For example, people generally care less about rewards they’ll get in a week, than about rewards they’ll get in a day.
Since, as the deadline for a task approaches, generally so do outcomes that are associated with it (i.e., related rewards and punishments), people generally value task outcomes more strongly closer to the deadline, and consequently become more motivated. This can lead, at least partially, to preference reversal, and consequently to transition from procrastination to action.
Furthermore, people generally display hyperbolic discounting in particular, which means that the further into the future an outcome is, the less the additional increase in time matters (e.g., the difference between an immediate outcome and one with a day’s delay is greater than between an outcome with a year’s delay and an outcome with a delay of a year and a day). Accordingly, the effects of discounting are more pronounced the shorter the remaining delay is, and this is most important when an outcome is expected to be achieved close to the deadline.
In addition, another related concept is purposeful delay, which in this context involves deliberately delaying until a deadline because doing so is expected to be more beneficial than not. This can happen, for example, when someone knows that a task might be canceled, so they believe it’s more efficient to wait until the deadline before committing resources to it. However, this type of behavior is not generally considered to be a form of procrastination, and would generally also not be considered a cause of the student syndrome.
Finally, the student syndrome and procrastination are also strongly related to the concept of a deadline action pacing style. This style involves completing most or all of the work in a short period of time just before deadlines, as opposed, for example, to completing them early or in a steady manner.
How to avoid the student syndrome
To avoid the student syndrome (i.e., to stop postponing things until right before the deadline), you should figure out what’s causing you to delay in the first place, and then use relevant anti-procrastination techniques, which will help you address the issue and take action in a timely manner.
The following are some of the anti-procrastination techniques that you can use.
Improve your planning:
- Set concrete goals for yourself. For example, instead of a vague goal, such as “study for my upcoming exam”, set a concrete goal, such as “on the week of my upcoming exam, go to the library every day after I finish my last class for the day, and spend at least 2 hours studying”.
- Break your tasks into small and manageable steps. For example, if you need to write an essay, you can start with steps such as figuring out the title, creating a rough outline, and finding five appropriate academic sources. Note that if the project in question is large, then you generally shouldn’t worry about figuring out all the steps to it from the start. Instead, start by identifying only the first few steps that you need to take, and then identify new steps as you make progress, to avoid feeling overwhelmed and getting stuck.
- Set intermediate milestones and deadlines for yourself. For example, if you have a single deadline for completing a large research paper, assign yourself additional deadlines along the way for completing specific parts of it.
- Identify your productivity cycles. People’s ability to handle certain tasks varies based on factors such as the time of day. For example, it may be the case that you’re best able to concentrate on difficult tasks early in the morning, before you’ve started dealing with emails or minor administrative aspects of your job. You should take this into account as much as possible when planning and scheduling your work.
Improve your environment:
- Change your environment to make it harder for yourself to procrastinate. For example, if you tend to procrastinate on writing essays because you keep browsing social media, turn off the internet connection on your computer before you get to work.
- Change your environment to make it easier for yourself to get started. For example, if you know that you’ll need to study for an exam tomorrow morning, organize all the relevant study material on your desk or in your bag before you go to bed.
- Change your environment to make it easier for you to keep going. For example, if you know that you’re likely to lose concentration if you get distracted while studying, go study in a quiet room and leave your phone outside.
Change your approach:
- Start with a tiny step. For example, if you need to write a paper, help yourself get started by committing to only write a single sentence at first. This can help you push yourself to get started on tasks, and often, once you do so, you’ll find it easy to keep going.
- Start with the best or worst part first. Some people find that starting with the most enjoyable or easiest task of the day helps them get going, while others find that getting the worst task out of the way first helps them avoid procrastinating over time. You can use either approach if you find that it works for you.
- Add a time delay before you procrastinate. If you can’t avoid procrastinating entirely, try committing to having a time delay before you indulge your impulse to do so. For example, this can involve counting to 10 before you’re allowed to open a new tab on the social media website that you usually use to procrastinate.
- Use the Pomodoro technique. This involves alternating between scheduled periods of study and rest. For example, you can study for 25-minute long stretches, with 5-minute breaks in between, and a longer 30-minute break after every 4 study sets that you complete.
Increase your motivation:
- Make your progress feel more rewarding. For example, you can gamify your work and try to achieve a streak of days on which you successfully manage to clear your to-do list, and potentially also give yourself some reward once you reach a sufficiently long streak.
- Make your work feel more enjoyable. For example, you can listen to music that you like while you work.
- Visualize your future self. For example, imagine yourself being rewarded with a good grade on a project that you completed on time, or conversely, imagine yourself having to handle the issues associated with missing the project’s deadline.
- Focus on your goals instead of on your tasks. For example, if you need to work on a task that you find boring, then instead of focusing on the task, try thinking about your goals for completing it, such as that you want to get a good grade.
Change your mindset:
- Give yourself permission to make mistakes. For example, if you’re working on an essay, accept the fact that your work likely won’t be perfect, especially at first. Furthermore, you can start by just writing a rough initial draft, and then go over it later to make improvements.
- Address your fears. If you’re procrastinating because you’re afraid of something, try to identify your fears and resolve them. For example, if you’re afraid that your writing won’t be good enough, you can say to yourself that your goal is to just start by getting something written down, and that you can always improve it later.
- Develop self-compassion. Self-compassion can help reduce your procrastination, as well as various issues that are associated with it, such as stress. It consists of three components that you should promote: self-kindness, which involves being nice to yourself, common humanity, which involves recognizing that everyone experiences challenges, and mindfulness, which involves accepting your emotions in a non-judgmental manner.
- Develop self-efficacy. Self-efficacy is the belief in your ability to perform the actions needed to achieve your goals. It can help you reduce your procrastination, as well as associated issues, such as anxiety. To develop self-efficacy, try to identify the various strategies that you can use to successfully complete your tasks on time, and think about your ability to execute those strategies successfully.
In addition, keep the following in mind:
- If you experience the student syndrome due to underlying issues such as ADHD, depression, or lack of sleep, you will likely need to resolve these issues first, using professional help if necessary, in order to avoid the student syndrome.
- You will likely need to use more than one anti-procrastination technique to completely avoid the student syndrome, but even just a few of them could make a huge difference when it comes to your ability to get things done on time.
- Different techniques work better for different people in different circumstances, so just because a certain technique works well for others, that doesn’t also mean that it will work well for you (and vice versa).
Overall, to avoid the student syndrome, you should figure out what’s causing you to delay in the first place, and then use relevant anti-procrastination techniques to address these causes. Such techniques include, for example, breaking large tasks into manageable steps, setting intermediate deadlines for yourself, visualizing your future self, and addressing your fears.
How to reduce the student syndrome in others
When it comes to helping other people avoid the student syndrome, for example if you’re a project manager, a teacher, or a parent, there are three main approaches you can use:
- An externally guided approach. This involves implementing relevant anti-procrastination techniques to reduce people’s student syndrome, without actively involving them in the process. For example, this can involve setting a series of intermediate project deadlines for all students in a course.
- An internally guided approach. This involves helping people avoid the student syndrome by themselves, with little to no external guidance. External guidance in this case might include something as minimal as mentioning the problem of student syndrome and telling people about a relevant resource such as this article.
- A joint approach. This involves giving people external guidance while also encouraging them to play an active role in reducing their student syndrome. For example, this can involve going over relevant anti-procrastination techniques with people, and helping them choose and implement their preferred ones.
None of these approaches is inherently superior to the others. Accordingly, you should decide which one to use based on factors such as the number of people that you’re trying to help and the type of relationship that you have with them. For example, if you’re a teacher trying to help 200 students in a college course, then you will likely need to use a different approach than if you’re a parent trying to help just your kid.
In this regard, an important factor to keep in mind is how independent the people in question are. In general, the more independent they are, the more involved they should be in the process of avoiding the student syndrome, since this can increase their motivation and make the process more effective, while potentially also leading to more self-development and growth over time. Furthermore, giving people a sense of control can also help reduce other issues that may lead to the student syndrome, such as resentment and rebellion.
Note that almost any type of relationship can be beneficial when it comes to helping people avoid the student syndrome. For example, a teacher will likely be in a good situation to influence a student’s academic situation, while a parent will likely be in a good situation to influence the student’s home life.
Furthermore, it can sometimes be beneficial to reach out to other stakeholders who can help. For example, if you’re a teacher, and you think that a student’s parents might be able to help them stop procrastinating, you might be able to reach out to them and explain the situation.
Finally, the following is a list of specific things that you can do to help people avoid the student syndrome:
- Explain what the student syndrome is.
- Help them understand that they display the student syndrome, for example by asking them guiding questions about their past behavior.
- Show them that this pattern of behavior can cause issues for them, for example when it comes to their academic performance, their career prospects, and their mental health.
- Explain what causes the student syndrome, and help them identify the specific causes of this behavior in their case.
- Point them in the direction of resources that can help them deal with the student syndrome, such as this article, or the guide to avoiding procrastination.
- Implement anti-procrastination techniques on their behalf, for example by breaking apart large tasks into manageable steps and setting intermediate deadlines.
- When setting general deadlines for people, understand that giving people more time to complete a task will not necessarily make it more likely that they will complete it in a timely manner, and it may even be counterproductive in some cases. This is associated with the concept of Parkinson’s law, which is the adage that “work expands so as to fill the time which is available for its completion”, and which signifies that the more time people dedicate in advance to a certain task, the longer it will take to complete it, even if it could have been completed in less time.
Overall, you can reduce people’s student syndrome in various ways, such as by helping them understand the causes of their behavior and helping them implement relevant anti-procrastination techniques. The specific approach that you should use depends on factors such as how autonomous the people in question are, how many people you’re trying to help, and what kind of relationship you have with them.
Summary and conclusions
- The student syndrome is a phenomenon where people delay doing things until right before the deadline.
- The student syndrome can lead to various issues, such as missed deadlines, low-quality work, interpersonal conflicts, and worse emotional wellbeing.
- People can display this type of behavior due to various causes, including a preference for working under pressure, motivational problems (e.g., discounting future outcomes), and psychological obstacles (e.g., anxiety), and some of these, in turn, may be caused or exacerbated by underlying issues, such as depression and lack of sleep.
- To avoid the student syndrome, you should figure out what’s causing you to delay in the first place, and then use relevant anti-procrastination techniques to address these causes, for example by breaking large tasks into manageable steps, setting intermediate deadlines for yourself, visualizing your future self, and addressing your fears.
- You can use a similar approach to reduce other people’s student syndrome, for example by helping them understand the causes of their behavior and helping them implement relevant anti-procrastination techniques.